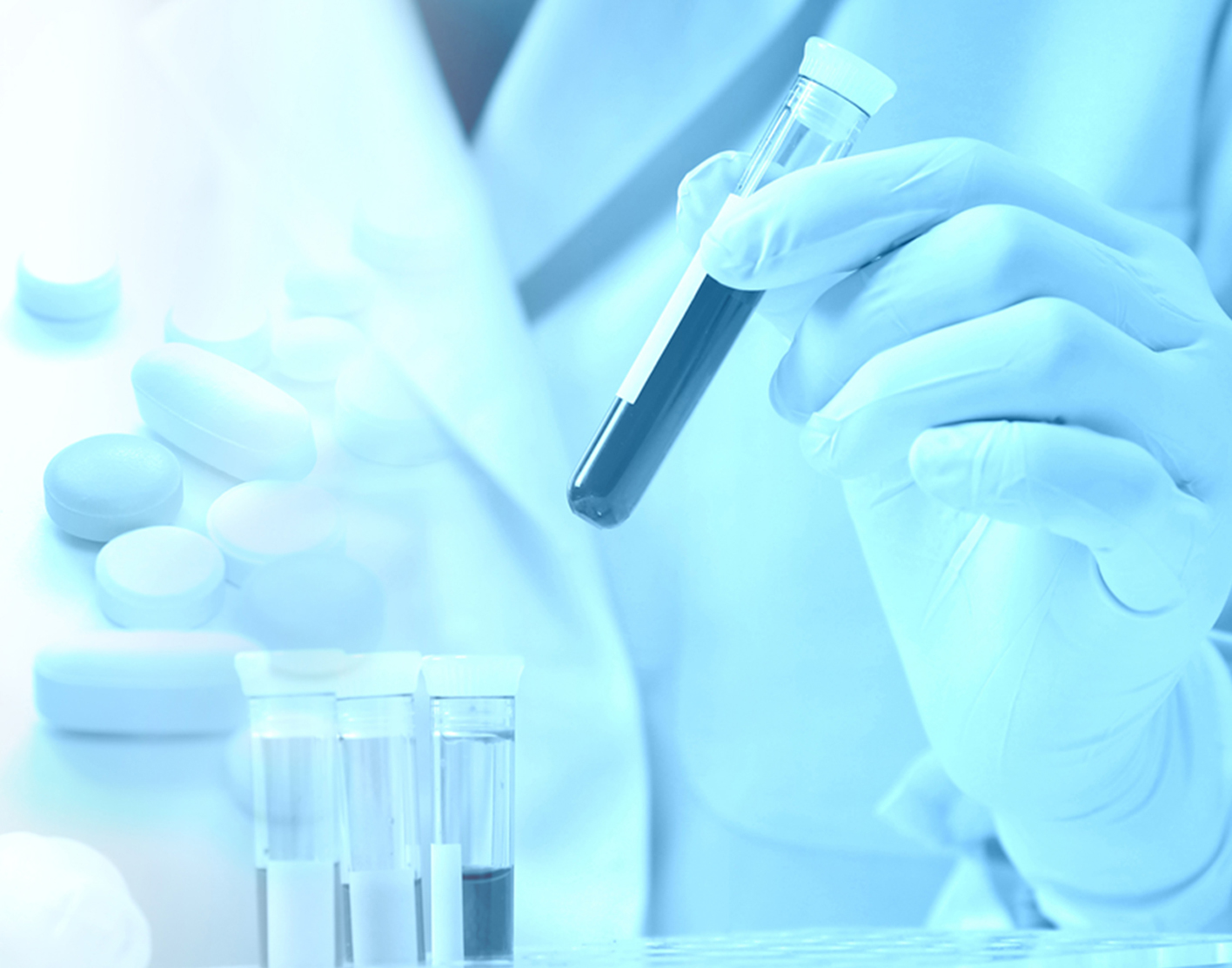
RPR test
Definition
RPR (rapid plasma reagin) is a screening test for
Alternative Names
Rapid plasma reagin test; Syphilis screening test
How the Test is Performed
A
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is usually needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or slight bruising. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
The RPR test can be used to screen for syphilis. It is used to screen people who have symptoms of sexually transmitted infections and is routinely used to screen pregnant women for the disease.
The test is also used to see how treatment for syphilis is working. After treatment with antibiotics, the levels of syphilis antibodies should fall. These levels can be monitored with another RPR test. Unchanged or rising levels can mean a persistent infection.
The test is similar to the
Normal Results
A negative test result is considered normal. However, the body does not always produce antibodies specifically in response to the syphilis bacteria, so the test is not always accurate. False-negatives may occur in people with early- and late-stage syphilis. More testing may be needed before ruling out syphilis.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive test result may mean that you have syphilis. If the screening test is positive, the next step is to confirm the diagnosis with a more specific test for syphilis, such as
How well the RPR test can detect syphilis depends on the stage of the infection. The test is most sensitive (almost 100%) during the middle (secondary and latent) stages of syphilis. It is less sensitive during the early (primary) and late (tertiary) stages of the infection.
Some conditions may cause a false-positive test, including:
Lyme disease - Certain types of pneumonia
Malaria - Pregnancy
Systemic lupus erythematosus and some other autoimmune disorders- Tuberculosis (TB)
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Radolf JD, Tramont EC, Salazar JC. Syphilis (Treponema pallidum). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 237.
US Preventive Services Task Force; Mangione CM, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for syphilis infection in nonpregnant adolescents and adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Reaffirmation Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2022;328(12):1243-1249. PMID: 36166020
Review Date: 26/08/2023
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright ©2019 A.D.A.M., Inc., as modified by University of California San Francisco. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Information developed by A.D.A.M., Inc. regarding tests and test results may not directly correspond with information provided by UCSF Health. Please discuss with your doctor any questions or concerns you may have.